사용자 관리
1-1. 사용자 생성 : useradd useradd -help
| useradd -d /home/ihd {userName} | {username} 을 생성하고 홈디렉토리를 /home/ihd |
| useradd -G whee,l ihd {userName} | 사용자의 2차 그룹을 wheel, ihd로 지정 |
| useradd -g tomcat {userName} | 사용자의 기본 그룹을 지정 |
| useradd -e YYYY-MM-DD {userName} | 사용자의 계정 만료일 설정 |
| useradd -f 일수 {userName} | 비밀번호 만료 후 계정 비활성화까지의 유예 기간 설정 (-1은 비활성화 안 함) |
Usage: useradd [options] LOGIN
useradd -D
useradd -D [options]
Options:
--badname do not check for bad names
-b, --base-dir BASE_DIR base directory for the home directory of the
new account
--btrfs-subvolume-home use BTRFS subvolume for home directory
-c, --comment COMMENT GECOS field of the new account
-d, --home-dir HOME_DIR home directory of the new account
-D, --defaults print or change default useradd configuration
-e, --expiredate EXPIRE_DATE expiration date of the new account
-f, --inactive INACTIVE password inactivity period of the new account
-g, --gid GROUP name or ID of the primary group of the new
account
-G, --groups GROUPS list of supplementary groups of the new
account
-h, --help display this help message and exit
-k, --skel SKEL_DIR use this alternative skeleton directory
-K, --key KEY=VALUE override /etc/login.defs defaults
-l, --no-log-init do not add the user to the lastlog and
faillog databases
-m, --create-home create the user's home directory
-M, --no-create-home do not create the user's home directory
-N, --no-user-group do not create a group with the same name as
the user
-o, --non-unique allow to create users with duplicate
(non-unique) UID
-p, --password PASSWORD encrypted password of the new account
-r, --system create a system account
-R, --root CHROOT_DIR directory to chroot into
-P, --prefix PREFIX_DIR prefix directory where are located the /etc/* files
-s, --shell SHELL login shell of the new account
-u, --uid UID user ID of the new account
-U, --user-group create a group with the same name as the user
-Z, --selinux-user SEUSER use a specific SEUSER for the SELinux user mapping
1-2. 패스워드 설정 : passwd passwd --help
| passwd -d {userName} | 패스워드 삭제 : 패스워드 입력없이 로그인 가능 |
| passwd -S {userName} | 사용자의 정보 확인 |
| passwd -l {userName} | 사용자 로그인 lock 일시적 제한 |
| passwd -u {userName} | lock 해제 |
| passwd -e {userName} | 사용자 비밀번호를 만료처리함 |
| passwd -x 90 -n 7 -w 10 -i 30 {userName} | • 최대 유효기간 90일 • 최소 유지기간 7일 • 만료 10일 전부터 경고 • 만료 후 30일 지나면 계정 잠금 |
Usage: passwd [OPTION...] <accountName>
-k, --keep-tokens keep non-expired authentication tokens
-d, --delete delete the password for the named account (root
only); also removes password lock if any
-l, --lock lock the password for the named account (root only)
-u, --unlock unlock the password for the named account (root only)
-e, --expire expire the password for the named account (root only)
-f, --force force operation
-x, --maximum=DAYS maximum password lifetime (root only)
-n, --minimum=DAYS minimum password lifetime (root only)
-w, --warning=DAYS number of days warning users receives before
password expiration (root only)
-i, --inactive=DAYS number of days after password expiration when an
account becomes disabled (root only)
-S, --status report password status on the named account (root
only)
--stdin read new tokens from stdin (root only)
1-3. 사용자 설정 변경 : usermod usermod -help
| usermod -l {새로운이름} {userName} | 사용자 이름 변경 |
| usermod -d /home/dev {userName} | 사용자의 홈디렉토리를 변경 |
| usermod -aG docker,developers {userName} | 사용자의 보조그룹을 docker, developers로 설정 |
| usermod -L {userName} usermod -U {userName} |
사용자 계정 잠금 사용자 계정 잠금 해제 |
Usage: usermod [options] LOGIN
Options:
-b, --badname allow bad names
-c, --comment COMMENT new value of the GECOS field
-d, --home HOME_DIR new home directory for the user account
-e, --expiredate EXPIRE_DATE set account expiration date to EXPIRE_DATE
-f, --inactive INACTIVE set password inactive after expiration
to INACTIVE
-g, --gid GROUP force use GROUP as new primary group
-G, --groups GROUPS new list of supplementary GROUPS
-a, --append append the user to the supplemental GROUPS
mentioned by the -G option without removing
the user from other groups
-h, --help display this help message and exit
-l, --login NEW_LOGIN new value of the login name
-L, --lock lock the user account
-m, --move-home move contents of the home directory to the
new location (use only with -d)
-o, --non-unique allow using duplicate (non-unique) UID
-p, --password PASSWORD use encrypted password for the new password
-R, --root CHROOT_DIR directory to chroot into
-P, --prefix PREFIX_DIR prefix directory where are located the /etc/* files
-s, --shell SHELL new login shell for the user account
-u, --uid UID new UID for the user account
-U, --unlock unlock the user account
-v, --add-subuids FIRST-LAST add range of subordinate uids
-V, --del-subuids FIRST-LAST remove range of subordinate uids
-w, --add-subgids FIRST-LAST add range of subordinate gids
-W, --del-subgids FIRST-LAST remove range of subordinate gids
-Z, --selinux-user SEUSER new SELinux user mapping for the user account
1-4.비밀번호 사용 기간 및 계정 만료 정책 설정 : chage chage -help
| chage -l {userName} | 사용자의 만료정보 확인 |
| chage -d 200 {userName} | 마지막 비밀번호 변경일 (Last password change date) 를 설정하는 옵션 chage -d 0 으로 하면 비밀번호를 오늘 날짜로 재설정 (즉시 변경 요구) |
| chage -E 2027-12-31 {userName} | 계정 만료일 지정 (YYYY-MM-DD 형식) |
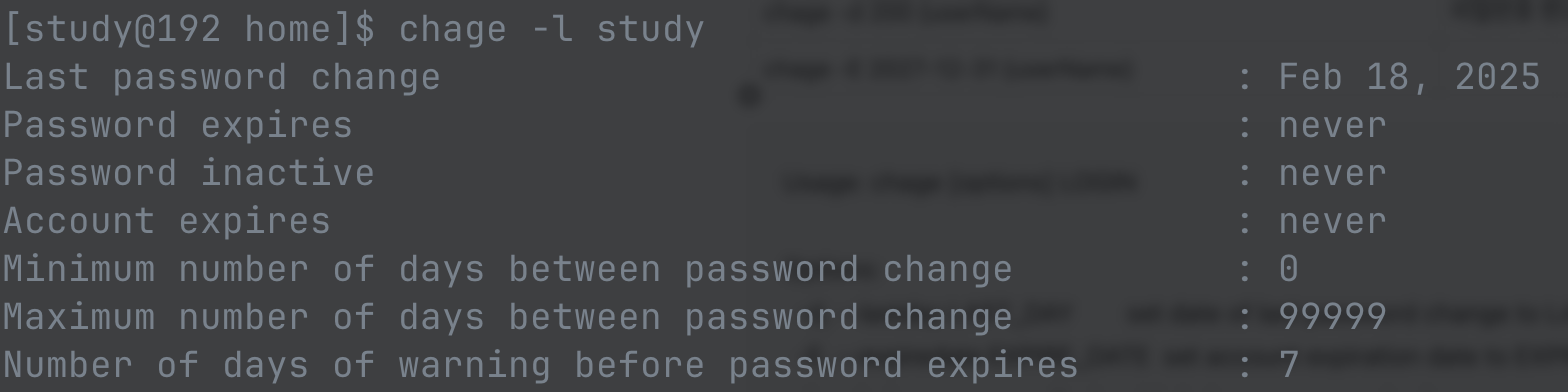

Usage: chage [options] LOGIN
Options:
-d, --lastday LAST_DAY set date of last password change to LAST_DAY
-E, --expiredate EXPIRE_DATE set account expiration date to EXPIRE_DATE
-h, --help display this help message and exit
-i, --iso8601 use YYYY-MM-DD when printing dates
-I, --inactive INACTIVE set password inactive after expiration
to INACTIVE
-l, --list show account aging information
-m, --mindays MIN_DAYS set minimum number of days before password
change to MIN_DAYS
-M, --maxdays MAX_DAYS set maximum number of days before password
change to MAX_DAYS
-R, --root CHROOT_DIR directory to chroot into
-W, --warndays WARN_DAYS set expiration warning days to WARN_DAYS
1-5. groupadd : groupadd groupadd -help
| groupadd {groupName} | 일반 그룹 생성 |
| groupadd -g 1500 {groupName} | GID 1500으로 그룹 생성 |
| groupadd -r {groupName} | 시스템 그룹으로 생성 |
Usage: groupadd [options] GROUP
Options:
-f, --force exit successfully if the group already exists,
and cancel -g if the GID is already used
-g, --gid GID use GID for the new group
-h, --help display this help message and exit
-K, --key KEY=VALUE override /etc/login.defs defaults
-o, --non-unique allow to create groups with duplicate
(non-unique) GID
-p, --password PASSWORD use this encrypted password for the new group
-r, --system create a system account
-R, --root CHROOT_DIR directory to chroot into
-P, --prefix PREFIX_DI directory prefix
-U, --users USERS list of user members of this group
1-6. groupmod : groupmod groupmod -help
| groupmod -g 2000 {groupName} | GID를 변경 |
| groupmod -n {new_groupName} {groupName} | 그룹명을 변경 |
Usage: groupmod [options] GROUP
Options:
-a, --append append the users mentioned by -U option to the group
without removing existing user members
-g, --gid GID change the group ID to GID
-h, --help display this help message and exit
-n, --new-name NEW_GROUP change the name to NEW_GROUP
-o, --non-unique allow to use a duplicate (non-unique) GID
-p, --password PASSWORD change the password to this (encrypted)
PASSWORD
-R, --root CHROOT_DIR directory to chroot into
-P, --prefix PREFIX_DIR prefix directory where are located the /etc/* files
-U, --users USERS list of user members of this group
1-7. 사용자 환경 설정 파일
| /etc/login.defs | 사용자 비밀번호 정책, UID/GID 범위, 패스워드 만료 정책 등을 정의 |
| /etc/default/useradd | useradd 명령 실행 시 기본값 설정 (홈 디렉토리, 셸 등) |
| /etc/skel/ | 신규 사용자의 홈 디렉토리에 복사될 기본 설정 파일들을 담고 있는 디렉토리 |
| /etc/passwd | 사용자 계정 정보 저장 파일 (계정명, UID, GID, 셸 등) |
| /etc/shadow | 사용자 비밀번호 정보 저장 (암호화된 비밀번호, 만료일 등) |
| /etc/group | 그룹 정보 저장 (그룹명, GID 등) |
/etc/login.defs
cat /etc/login.defs
#
# Please note that the parameters in this configuration file control the
# behavior of the tools from the shadow-utils component. None of these
# tools uses the PAM mechanism, and the utilities that use PAM (such as the
# passwd command) should therefore be configured elsewhere. Refer to
# /etc/pam.d/system-auth for more information.
#
#
# Delay in seconds before being allowed another attempt after a login failure
# Note: When PAM is used, some modules may enforce a minimum delay (e.g.
# pam_unix(8) enforces a 2s delay)
#
#FAIL_DELAY 3
# Currently FAILLOG_ENAB is not supported
#
# Enable display of unknown usernames when login(1) failures are recorded.
#
#LOG_UNKFAIL_ENAB no
# Currently LOG_OK_LOGINS is not supported
# Currently LASTLOG_ENAB is not supported
#
# Limit the highest user ID number for which the lastlog entries should
# be updated.
#
# No LASTLOG_UID_MAX means that there is no user ID limit for writing
# lastlog entries.
#
#LASTLOG_UID_MAX
# Currently MAIL_CHECK_ENAB is not supported
# Currently OBSCURE_CHECKS_ENAB is not supported
# Currently PORTTIME_CHECKS_ENAB is not supported
# Currently QUOTAS_ENAB is not supported
# Currently SYSLOG_SU_ENAB is not supported
#
# Enable "syslog" logging of newgrp(1) and sg(1) activity.
#
#SYSLOG_SG_ENAB yes
# Currently CONSOLE is not supported
# Currently SULOG_FILE is not supported
# Currently MOTD_FILE is not supported
# Currently ISSUE_FILE is not supported
# Currently TTYTYPE_FILE is not supported
# Currently FTMP_FILE is not supported
# Currently NOLOGINS_FILE is not supported
# Currently SU_NAME is not supported
# *REQUIRED*
# Directory where mailboxes reside, _or_ name of file, relative to the
# home directory. If you _do_ define both, MAIL_DIR takes precedence.
#
MAIL_DIR /var/spool/mail
#MAIL_FILE .mail
#
# If defined, file which inhibits all the usual chatter during the login
# sequence. If a full pathname, then hushed mode will be enabled if the
# user's name or shell are found in the file. If not a full pathname, then
# hushed mode will be enabled if the file exists in the user's home directory.
#
#HUSHLOGIN_FILE .hushlogin
#HUSHLOGIN_FILE /etc/hushlogins
# Currently ENV_TZ is not supported
# Currently ENV_HZ is not supported
#
# The default PATH settings, for superuser and normal users.
#
# (they are minimal, add the rest in the shell startup files)
#ENV_SUPATH PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
#ENV_PATH PATH=/bin:/usr/bin
#
# Terminal permissions
#
# TTYGROUP Login tty will be assigned this group ownership.
# TTYPERM Login tty will be set to this permission.
#
# If you have a write(1) program which is "setgid" to a special group
# which owns the terminals, define TTYGROUP as the number of such group
# and TTYPERM as 0620. Otherwise leave TTYGROUP commented out and
# set TTYPERM to either 622 or 600.
#
#TTYGROUP tty
#TTYPERM 0600
# Currently ERASECHAR, KILLCHAR and ULIMIT are not supported
# Default initial "umask" value used by login(1) on non-PAM enabled systems.
# Default "umask" value for pam_umask(8) on PAM enabled systems.
# UMASK is also used by useradd(8) and newusers(8) to set the mode for new
# home directories if HOME_MODE is not set.
# 022 is the default value, but 027, or even 077, could be considered
# for increased privacy. There is no One True Answer here: each sysadmin
# must make up their mind.
UMASK 022
# HOME_MODE is used by useradd(8) and newusers(8) to set the mode for new
# home directories.
# If HOME_MODE is not set, the value of UMASK is used to create the mode.
HOME_MODE 0700
# Password aging controls:
#
# PASS_MAX_DAYS Maximum number of days a password may be used.
# PASS_MIN_DAYS Minimum number of days allowed between password changes.
# PASS_MIN_LEN Minimum acceptable password length.
# PASS_WARN_AGE Number of days warning given before a password expires.
#
PASS_MAX_DAYS 99999
PASS_MIN_DAYS 0
PASS_WARN_AGE 7
# Currently PASS_MIN_LEN is not supported
# Currently SU_WHEEL_ONLY is not supported
# Currently CRACKLIB_DICTPATH is not supported
#
# Min/max values for automatic uid selection in useradd(8)
#
UID_MIN 1000
UID_MAX 60000
# System accounts
SYS_UID_MIN 201
SYS_UID_MAX 999
# Extra per user uids
SUB_UID_MIN 100000
SUB_UID_MAX 600100000
SUB_UID_COUNT 65536
#
# Min/max values for automatic gid selection in groupadd(8)
#
GID_MIN 1000
GID_MAX 60000
# System accounts
SYS_GID_MIN 201
SYS_GID_MAX 999
# Extra per user group ids
SUB_GID_MIN 100000
SUB_GID_MAX 600100000
SUB_GID_COUNT 65536
#
# Max number of login(1) retries if password is bad
#
#LOGIN_RETRIES 3
#
# Max time in seconds for login(1)
#
#LOGIN_TIMEOUT 60
# Currently PASS_CHANGE_TRIES is not supported
# Currently PASS_ALWAYS_WARN is not supported
# Currently PASS_MAX_LEN is not supported
# Currently CHFN_AUTH is not supported
#
# Which fields may be changed by regular users using chfn(1) - use
# any combination of letters "frwh" (full name, room number, work
# phone, home phone). If not defined, no changes are allowed.
# For backward compatibility, "yes" = "rwh" and "no" = "frwh".
#
#CHFN_RESTRICT rwh
# Currently LOGIN_STRING is not supported
# Currently MD5_CRYPT_ENAB is not supported
#
# If set to MD5, MD5-based algorithm will be used for encrypting password
# If set to SHA256, SHA256-based algorithm will be used for encrypting password
# If set to SHA512, SHA512-based algorithm will be used for encrypting password
# If set to BLOWFISH, BLOWFISH-based algorithm will be used for encrypting password
# If set to DES, DES-based algorithm will be used for encrypting password (default)
#
ENCRYPT_METHOD SHA512
#
# Only works if ENCRYPT_METHOD is set to SHA256 or SHA512.
#
# Define the number of SHA rounds.
# With a lot of rounds, it is more difficult to brute-force the password.
# However, more CPU resources will be needed to authenticate users if
# this value is increased.
#
# If not specified, the libc will choose the default number of rounds (5000).
# The values must be within the 1000-999999999 range.
#
SHA_CRYPT_MAX_ROUNDS 100000
# Currently SHA_CRYPT_MIN_ROUNDS is not supported
# Currently BCRYPT_MIN_ROUNDS and BCRYPT_MAX_ROUNDS are not supported
# Currently CONSOLE_GROUPS is not supported
#
# Should login be allowed if we can't cd to the home directory?
# Default is yes.
#
#DEFAULT_HOME yes
# Currently ENVIRON_FILE is not supported
#
# If defined, this command is run when removing a user.
# It should remove any at/cron/print jobs etc. owned by
# the user to be removed (passed as the first argument).
#
#USERDEL_CMD /usr/sbin/userdel_local
#
# Enables userdel(8) to remove user groups if no members exist.
#
USERGROUPS_ENAB yes
#
# If set to a non-zero number, the shadow utilities will make sure that
# groups never have more than this number of users on one line.
# This permits to support split groups (groups split into multiple lines,
# with the same group ID, to avoid limitation of the line length in the
# group file).
#
# 0 is the default value and disables this feature.
#
#MAX_MEMBERS_PER_GROUP 0
#
# If useradd(8) should create home directories for users by default (non
# system users only).
# This option is overridden with the -M or -m flags on the useradd(8)
# command-line.
#
CREATE_HOME yes
#
# Force use shadow, even if shadow passwd & shadow group files are
# missing.
#
#FORCE_SHADOW yes
#
# Select the HMAC cryptography algorithm.
# Used in pam_timestamp module to calculate the keyed-hash message
# authentication code.
#
# Note: It is recommended to check hmac(3) to see the possible algorithms
# that are available in your system.
#
HMAC_CRYPTO_ALGO SHA512
/etc/default/useradd
cat /etc/default/useradd
# useradd defaults file
GROUP=100
HOME=/home
INACTIVE=-1
EXPIRE=
SHELL=/bin/bash
SKEL=/etc/skel
CREATE_MAIL_SPOOL=yes
/etc/passwd
cat /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin
ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin
nobody:x:65534:65534:Kernel Overflow User:/:/sbin/nologin
tss:x:59:59:Account used for TPM access:/:/usr/sbin/nologin
systemd-coredump:x:999:997:systemd Core Dumper:/:/sbin/nologin
dbus:x:81:81:System message bus:/:/sbin/nologin
polkitd:x:998:996:User for polkitd:/:/sbin/nologin
sssd:x:997:995:User for sssd:/:/sbin/nologin
chrony:x:996:994:chrony system user:/var/lib/chrony:/sbin/nologin
sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/usr/share/empty.sshd:/usr/sbin/nologin
study:x:1000:1000::/home/study:/bin/bash
rtkit:x:172:172:RealtimeKit:/:/sbin/nologin
pipewire:x:995:992:PipeWire System Daemon:/run/pipewire:/usr/sbin/nologin
geoclue:x:994:991:User for geoclue:/var/lib/geoclue:/sbin/nologin
flatpak:x:993:990:User for flatpak system helper:/:/sbin/nologin
stapunpriv:x:159:159:systemtap unprivileged user:/var/lib/stapunpriv:/sbin/nologin
pesign:x:992:989:Group for the pesign signing daemon:/run/pesign:/sbin/nologin
postgres:x:26:26:PostgreSQL Server:/var/lib/pgsql:/bin/bash
bang:x:1001:1001::/home/bang:/bin/bash
/etc/shadow
cat /etc/shadow
root:$6$6TrkZVZBIYQWrl8s$DOn8mOU5.WPJWh7SVU0KfIo3ohBAy0tXR4aqXv2Tn7cuNb0IL6TjZRXJnV14HO9kNMFb6d8PJAxCJ5T6iJ0VA0::0:99999:7:::
bin:*:19820:0:99999:7:::
daemon:*:19820:0:99999:7:::
adm:*:19820:0:99999:7:::
lp:*:19820:0:99999:7:::
sync:*:19820:0:99999:7:::
shutdown:*:19820:0:99999:7:::
halt:*:19820:0:99999:7:::
mail:*:19820:0:99999:7:::
operator:*:19820:0:99999:7:::
games:*:19820:0:99999:7:::
ftp:*:19820:0:99999:7:::
nobody:*:19820:0:99999:7:::
tss:!!:20137::::::
systemd-coredump:!!:20137::::::
dbus:!!:20137::::::
polkitd:!!:20137::::::
sssd:!!:20137::::::
chrony:!!:20137::::::
sshd:!!:20137::::::
study:$6$rounds=100000$/8uxdGZjN/C/PDW3$AOoNz47p32m75PUDiIfhyS9jpASIc/wQNgm0ZyazQgRDDuRBDI8N4CfkuYnRUlk38pzapNv5iYMYU.4Gz3h4G0:20189:0:99999:7:::
rtkit:!!:20145::::::
pipewire:!!:20145::::::
geoclue:!!:20145::::::
flatpak:!!:20145::::::
stapunpriv:!*:20152::::::
pesign:!!:20152::::::
postgres:$6$rounds=100000$Ok2Fay4nx3qeJggk$MqZ35gQV004SBsA8JdFH6YjC4/dFqxgZOhIkcMBunBC98VlfJY3ywBOZSuXPm.J7rc0T8rn5hc8hnb1brcYf00:20189::::::
bang:!!:20189:0:99999:7:::
사용자 및 그룹정보 관련 명령어
| whoami | 현재 셸에서 로그인한 사용자 이름 출력 |
| users | |
| who | 시스템에 로그인 중인 전체 사용자 목록 확인 |
| id | UID, GID, 그룹 등 사용자 상세 정보 출력 |
| id {userName} | 특정 사용자의 UID, GID, 그룹 확인 |
| users |
로그인된 사용자 이름만 출력 |
| groups |
현재 사용자가 속한 그룹 출력 |




'자격증' 카테고리의 다른 글
| AWS SAA-C03 Dump 51-100 (0) | 2026.01.29 |
|---|---|
| AWS SAA-C03 Dump 1-50 (1) | 2026.01.28 |
| 정렬 알고리즘 (0) | 2024.10.17 |
| 소프트웨어 보안 구축 (9) | 2024.10.16 |
| SQL응용 (4) | 2024.10.16 |

